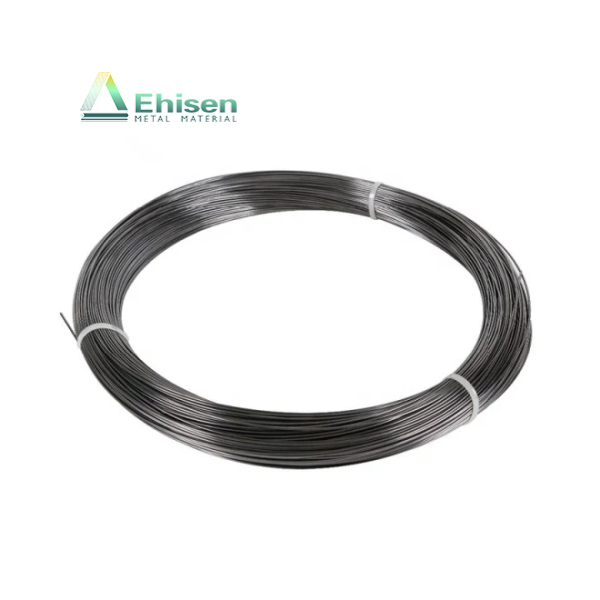
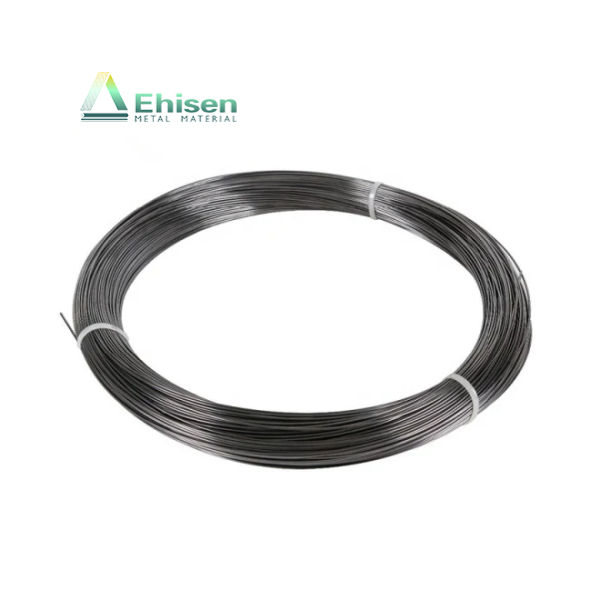
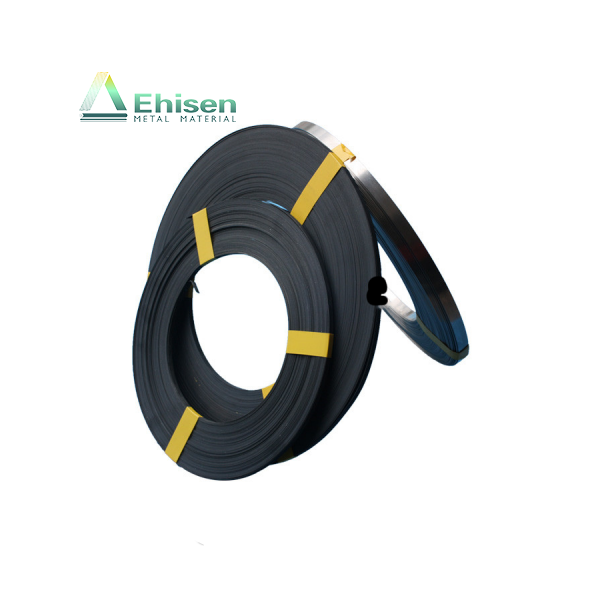
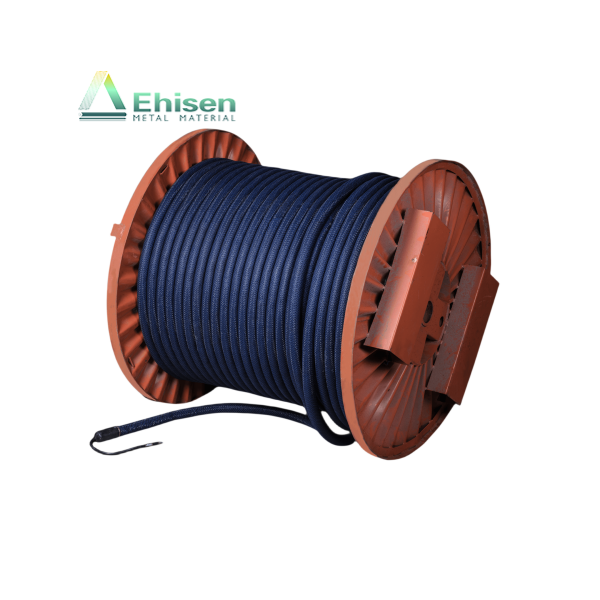
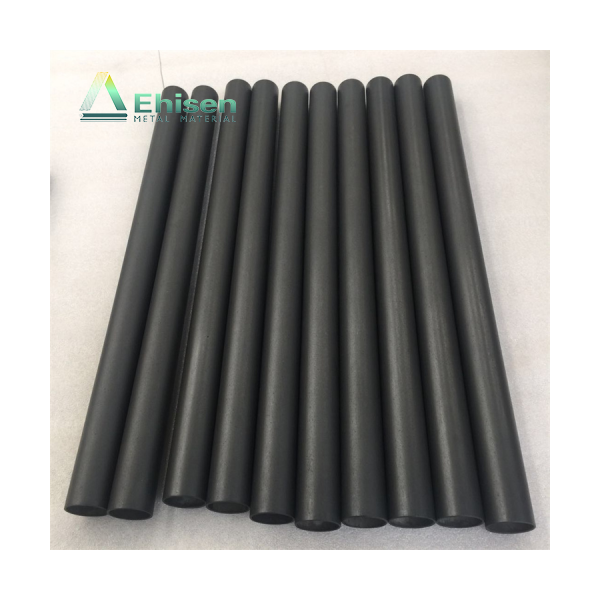
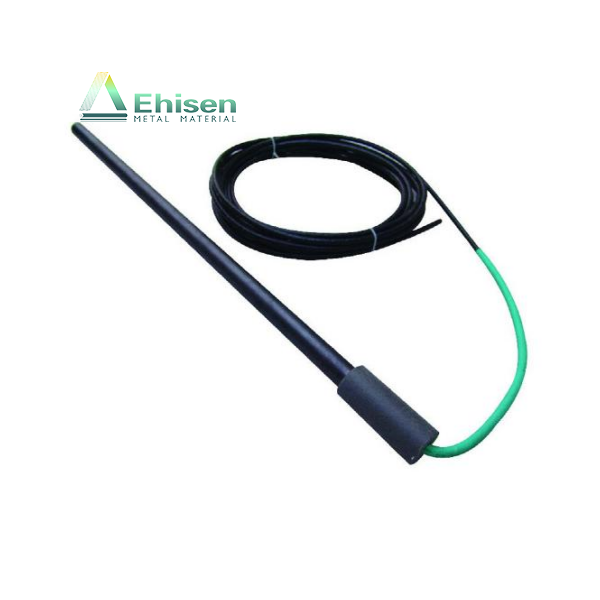
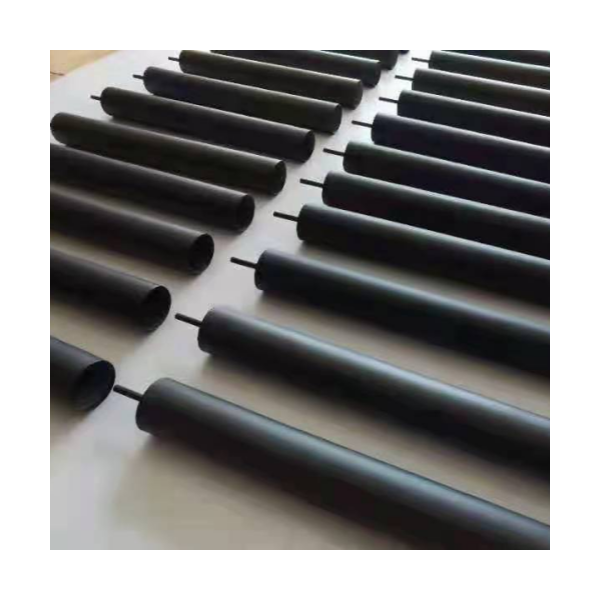
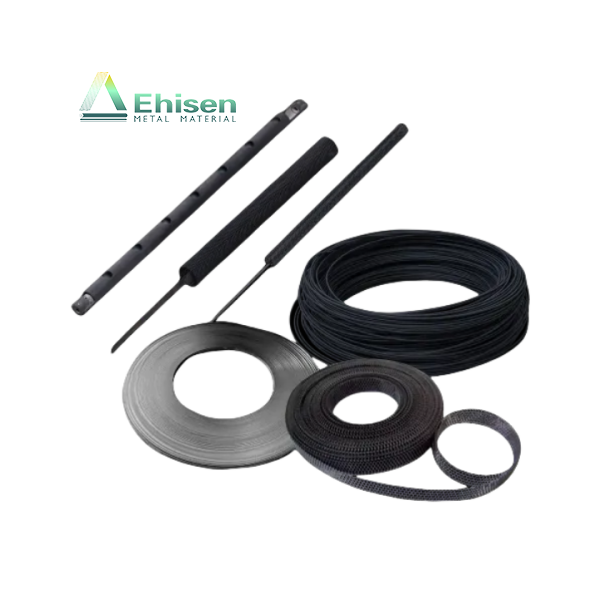
鈦陽(yáng)極是強(qiáng)制電流陰極保護(hù)(ICCP)系統(tǒng)中的關(guān)鍵組成部分,廣泛應(yīng)用于海水、潮濕土壤等高腐蝕性環(huán)境中,用于保護(hù)金屬結(jié)構(gòu)免受腐蝕,如海底管道、儲(chǔ)罐底板和海上平臺(tái)。
憑借優(yōu)異的耐腐蝕性與穩(wěn)定的導(dǎo)電性能,鈦陽(yáng)極通過施加可控直流電流,有效中斷腐蝕電化學(xué)反應(yīng),長(zhǎng)期保障結(jié)構(gòu)安全與完整性。
Titanium anodes are vital in impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) systems. They protect metal structures—such as pipelines, storage tanks, and offshore platforms—from corrosion in aggressive environments like seawater and moist soil.
With exceptional corrosion resistance and stable conductivity, titanium anodes deliver a controlled current that halts electrochemical corrosion reactions, ensuring long-term structural integrity and safety.
典型應(yīng)用范圍 | Application Scenarios
海洋工程:LNG接收站鋼樁、跨海大橋橋墩
Offshore engineering: LNG terminal piles, cross-sea bridge foundations
能源運(yùn)輸:沙漠或海底原油管線、儲(chǔ)罐底板
Energy transport: desert/subsea crude pipelines, tank bottoms
化工防腐:酸液儲(chǔ)罐內(nèi)壁、PTA反應(yīng)釜陰極保護(hù)
Chemical protection: acid tank linings, PTA reactor cathodic systems
新能源設(shè)施:海上風(fēng)電升壓站、氫能儲(chǔ)運(yùn)管網(wǎng)
Emerging energy: offshore wind platforms, hydrogen storage & transport systems
? 核心優(yōu)勢(shì) | Key Advantages
1. 超長(zhǎng)壽命,穩(wěn)定可靠
? 使用壽命遠(yuǎn)超傳統(tǒng)犧牲陽(yáng)極
? 可長(zhǎng)期耐受鹽霧、酸雨、海水等腐蝕環(huán)境
Long service life and reliability
? Outlasts traditional sacrificial anodes
? Resists salt spray, acid rain, and seawater for years
2. 精準(zhǔn)防護(hù),全域覆蓋
? 電流輸出精準(zhǔn),自動(dòng)調(diào)節(jié)
? 適配復(fù)雜結(jié)構(gòu),無(wú)死角防護(hù)(如焊縫、底板邊角)
Accurate protection with full coverage
? Delivers precisely regulated current
? Effective even on complex geometries (e.g., welds, base corners)
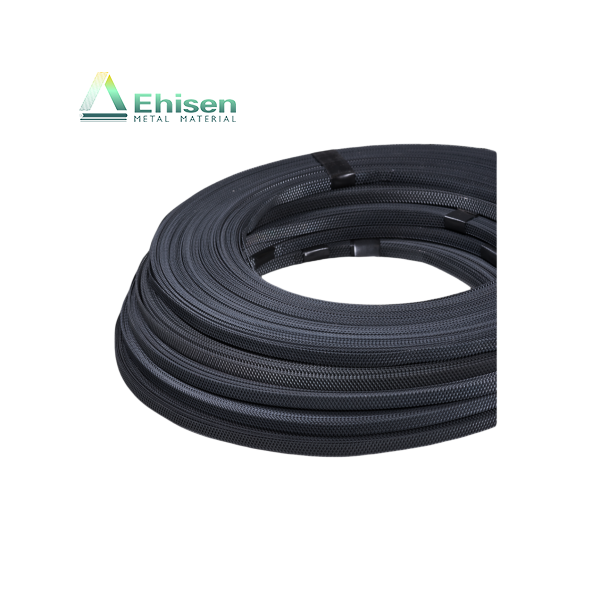
3. 柔性設(shè)計(jì),施工便捷
? 可纏繞或彎曲,貼合異形設(shè)備
? 降低施工難度,無(wú)需大面積開挖
Flexible design for easier installation
? Bendable and adaptable to irregular shapes
? Minimizes excavation and simplifies deployment
4. 經(jīng)濟(jì)高效,維護(hù)省心
? 后期維護(hù)成本低
? 保障重大設(shè)施長(zhǎng)期運(yùn)行安全(如跨海大橋、石油罐區(qū))
Cost-effective and low maintenance
? Reduces long-term operating expenses
? Enhances safety and uptime of major assets (e.g., sea-crossing bridges, oil terminals)